[C#] Lambda의 원리와 캡처 시 임시 클래스 생성에 대해서
카테고리: CSharp
태그: Lambda
Lambda의 원리와 캡처 시 임시 클래스 생성에 대해서 공부하고 정리한 글입니다.
람다식의 원리
- 람다식을 사용하면 컴파일러가 임시 클래스가 하나 생성시켜준다
- 람다식 안의 코드는 임시 클래스의 멤버 함수로 변하게 된다
- 캡처가 이루어지는 경우 임시 클래스의 멤버로 가지게 된다
- 비정적 변수를 캡처하여 임시 클래스가 생성된 경우 람다식이 있는 Scope를 진입할 때마다 임시 클래스를 동적 할당하게 된다
- 람다식을 사용하는 경우 delegate 객체를 동적 할당하게 된다
- 람다식을 호출하면 임시 클래스의 멤버 함수가 호출된다
각종 예시
- 밑에 예시를 보면서 캡처방식마다 어떻게 임시 클래스가 생성되는지 확인하자
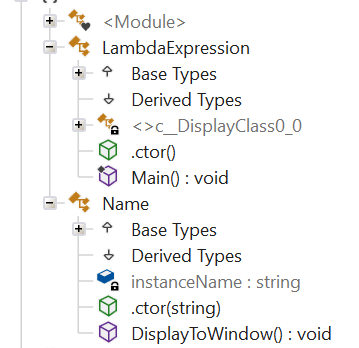
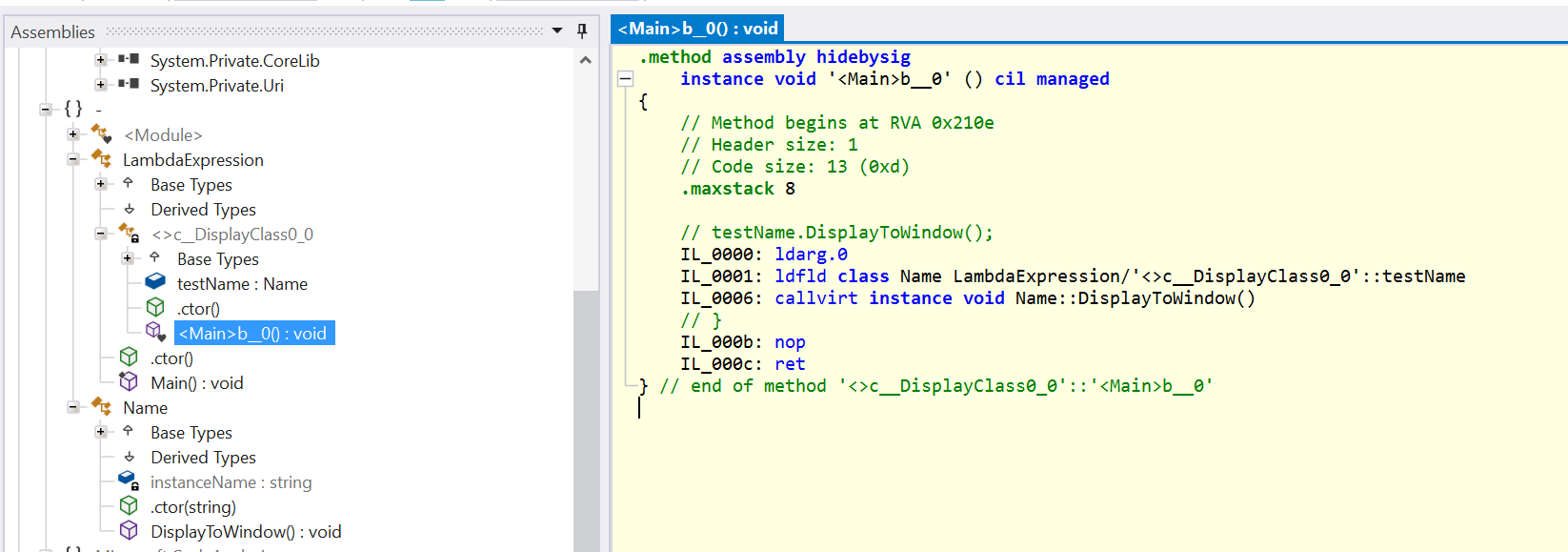
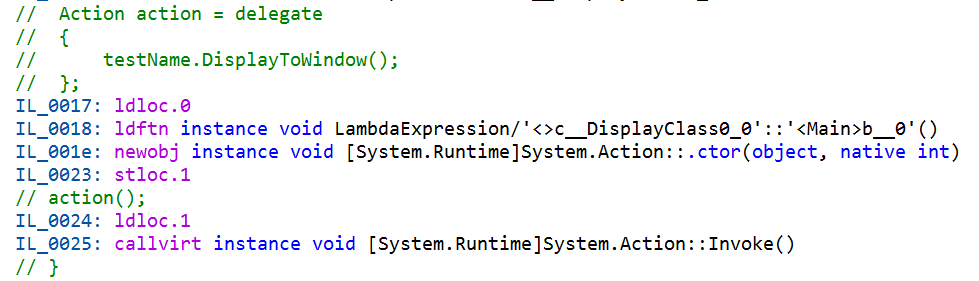
케이스 1 : 하나의 람다식이 존재하는 경우
public class Name
{
private string instanceName;
public Name(string name)
{
this.instanceName = name;
}
public void DisplayToWindow()
{
Console.WriteLine(this.instanceName);
}
}
public class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Name testName = new Name("Koani");
Action showMethod = () => testName.DisplayToWindow();
showMethod();
}
}
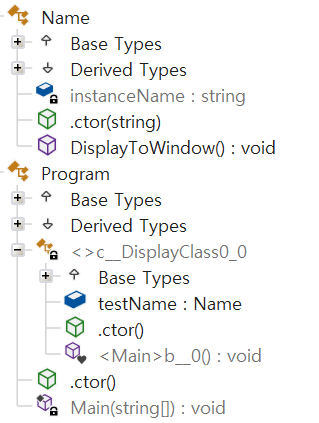
- 람다식의 코드를 가지는 임시 클래스 하나가 생성되게 된다
케이스 2 : 여러 람다식이 존재하는 경우
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int testName = 5;
Action showMethod = () => { ++testName; Console.WriteLine(testName); };
Action showMethod2 = () => { Console.WriteLine(testName); };
Action showMethod3 = () => { Console.WriteLine(testName); };
Action showMethod4 = () => { Console.WriteLine(testName); };
Action showMethod5 = () => { Console.WriteLine(testName); };
Action showMethod6 = () => { Console.WriteLine(testName); };
Action showMethod7 = () => { Console.WriteLine(testName); };
Action showMethod8 = () => { Console.WriteLine(testName); };
Action showMethod9 = () => { Console.WriteLine(testName); };
showMethod();
showMethod2();
}
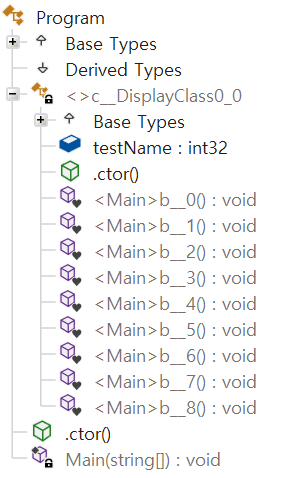
- 여러 람다식마다 함수가 생성된다
케이스 3 : 여러 람다식이 다른 비정적 변수를 캡처하는 경우
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int i = 256;
string s = "string";
double d = 135.513;
Action showMethod1 = () => { Console.WriteLine(i); };
Action showMethod2 = () => { Console.WriteLine(s); Console.WriteLine(++i); };
Action showMethod3 = () => { Console.WriteLine(d += 123.456); Console.WriteLine(s += "add"); Console.WriteLine(++i); };
showMethod1();
showMethod2();
showMethod3();
showMethod3();
showMethod2();
showMethod1();
}
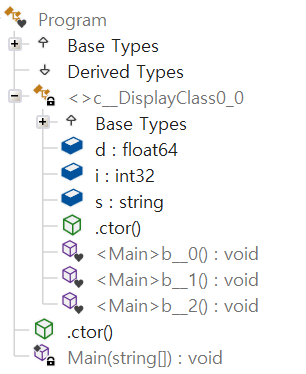
- 다른 비정적 변수를 캡처한다고 해서 임시 클래스가 나뉘어지지 않는다
케이스 4 : 비정적 변수를 캡처하고 정적 변수를 사용하는 경우
public class TestClass
{
int i = 256;
double d = 135.513;
public void Test()
{
Action showMethod1 = () => { Console.WriteLine(++Program.staticInt); };
Action showMethod2 = () => { Console.WriteLine(showMethod1); Console.WriteLine(++i); };
Action showMethod3 = () => { Console.WriteLine(d += 123.456); Console.WriteLine(showMethod2); Console.WriteLine(showMethod2); };
Action showMethod4 = () => { Console.WriteLine(TestClass222.staticDouble += 12.45); };
showMethod1();
showMethod2();
showMethod3();
showMethod4();
}
}
public class TestClass222
{
public static double staticDouble = 123.456;
}
public class Program
{
public static int staticInt = 132;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
TestClass test = new TestClass();
test.Test();
}
}
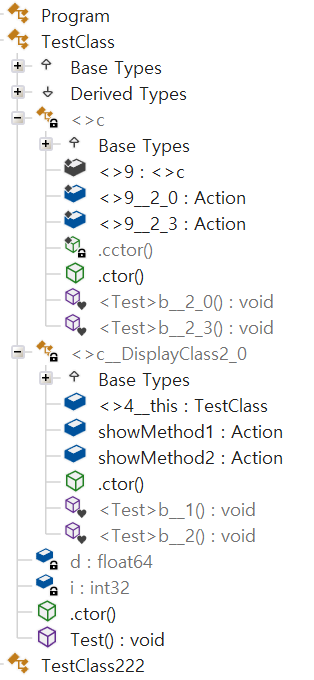
- 정적 변수와 같이 같은 Scope(범위)에 없는 경우 따로 임시 클래스가 만들어 진다
- 근데 케이스 5 는 정적 변수를 사용했음에도 클래스가 나뉘어 지지 않는다
케이스 5 : 하나의 람다식에서 비정적 변수를 캡처하고 정적 변수를 사용하는 경우
public class TestClass
{
int i = 256;
double d = 135.513;
public void Test()
{
Action showMethod1 = () => { Console.WriteLine(d += 123.456); Console.WriteLine(++Program.staticInt); };
Action showMethod2 = () => { Console.WriteLine(showMethod1); Console.WriteLine(++i); };
Action showMethod3 = () => { Console.WriteLine(d += 123.456); Console.WriteLine(showMethod2); Console.WriteLine(showMethod2); };
Action showMethod4 = () => { Console.WriteLine(TestClass222.staticDouble += 12.45); Console.WriteLine(d += 123.456); };
showMethod1();
showMethod2();
showMethod3();
showMethod4();
}
}
public class TestClass222
{
public static double staticDouble = 123.456;
}
public class Program
{
public static int staticInt = 132;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
TestClass test = new TestClass();
test.Test();
}
}
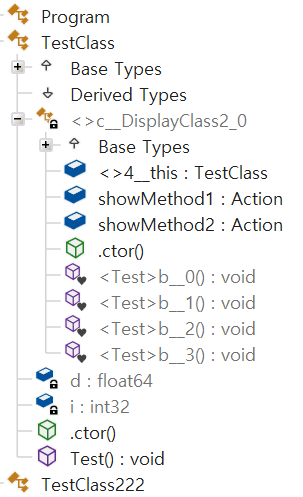
- 정적 변수만 사용되는 경우 정적 클래스가 따로 만들어지고 만약 비정적 변수를 같이 캡처하는 경우 하나의 임시 클래스로 합쳐지는 것으로 보인다
케이스 6 : 다른 클래스 같은 동작의 람다 함수인 경우 (캡처 X)
public class TestClass
{
public void Test()
{
Action showMethod1 = () => { Console.WriteLine(); };
showMethod1();
}
}
public class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
TestClass test = new TestClass();
test.Test();
Action showMethod1 = () => { Console.WriteLine(); };
showMethod1();
}
}
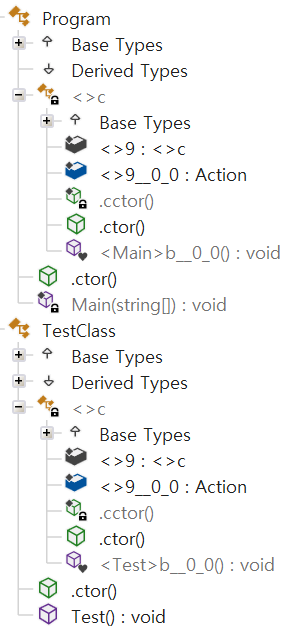
- 같은 동작의 함수라고 해서 같은 임시 클래스를 사용하지는 않는다 (2개의 임시 클래스가 생성됨)
케이스 7 : 다른 클래스 같은 동작의 람다 함수인 경우 (비정적 변수 캡처, 정적 변수 사용)
public class TestClass
{
int i = 256;
double d = 135.513;
public void Test()
{
Action showMethod1 = () => { Console.WriteLine(++Program.staticInt); };
Action showMethod2 = () => { Console.WriteLine(showMethod1); Console.WriteLine(++i); };
Action showMethod3 = () => { Console.WriteLine(d += 123.456); Console.WriteLine(showMethod2); Console.WriteLine(showMethod2); };
Action showMethod4 = () => { Console.WriteLine(TestClass222.staticDouble += 12.45); };
showMethod1();
showMethod2();
showMethod3();
showMethod4();
}
}
public class TestClass222
{
public static double staticDouble = 123.456;
}
public class Program
{
public static int staticInt = 132;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
TestClass test = new TestClass();
test.Test();
int i = 256;
double d = 135.513;
Action showMethod1 = () => { Console.WriteLine(++staticInt); };
Action showMethod2 = () => { Console.WriteLine(showMethod1); Console.WriteLine(++i); };
Action showMethod3 = () => { Console.WriteLine(d += 123.456); Console.WriteLine(showMethod2); Console.WriteLine(showMethod2); };
Action showMethod4 = () => { Console.WriteLine(TestClass222.staticDouble += 12.45); };
showMethod1();
showMethod2();
showMethod3();
showMethod4();
}
}
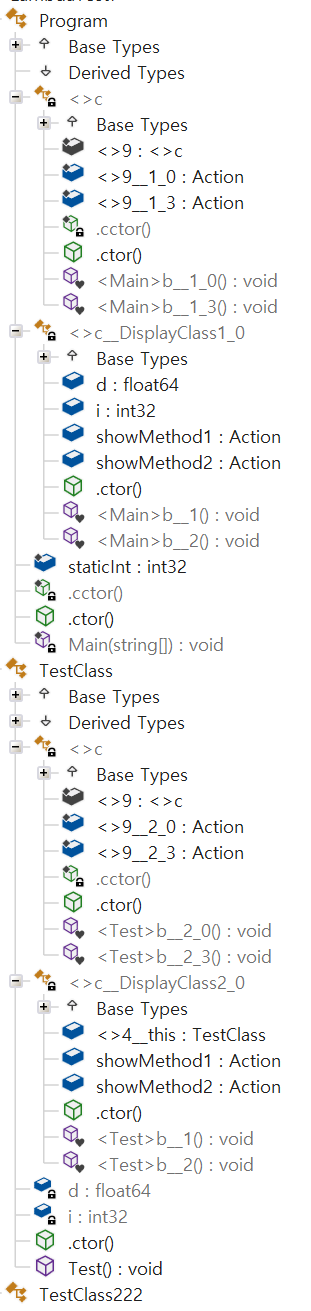
- 코드가 중복이 되더라도 서로 Scope가 다르면 임시 클래스가 따로 생긴다
참조
💻 열심히 공부해서 작성 중이니 오류나 틀린 부분이 있을 경우
언제든지 댓글 혹은 메일로 알려주시면 감사하겠습니다! 😸

댓글 남기기